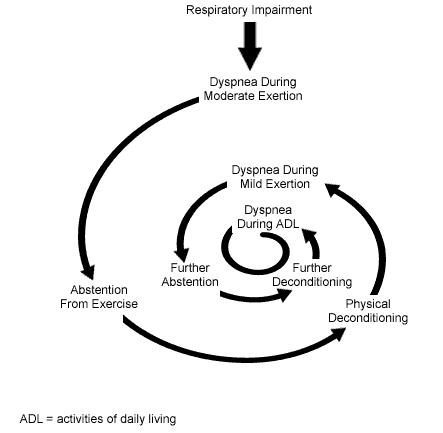
 Respiratory failure occurs when insufficient gas exchange is occurring in the body to adequately perfuse (oxygenate) the tissues and organs of the body. This results in blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels no longer being maintained within normal ranges. The detected lowered blood oxygen levels are called hypoxia and the rising carbon dioxide level is called hypercapnia.
Respiratory failure occurs when insufficient gas exchange is occurring in the body to adequately perfuse (oxygenate) the tissues and organs of the body. This results in blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels no longer being maintained within normal ranges. The detected lowered blood oxygen levels are called hypoxia and the rising carbon dioxide level is called hypercapnia.
Causes:
- parenchymal lung disease is a condition affecting the epithelium of the alveoli, associated capillaries and lung tissues causing gas exchange to be hindered.
- respiratory distress symdrome resulting in severe inflammation of the lung tissue
- pneumonia – infection of the lungs causing a decrease in effective gas exchange
- Cystic fibrosis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Pulmonary edema (fluid retention in the lungs)
- Cerebrovascular accident, CVA (stroke)
- Congestive heart failure
Treatment:
Treatments to manage underlying causes, such as antibiotic for bacterial pneumonia. Additionally, the use of oxygen via mask or nasal prongs to increase the concentration oxygen molecules within the air breathed in to enhance gas exchange at the lung-alveolar barrier and positioning patients in the prone (on stomach) position to improve oxygenation.
Brazzi, Luca, Di Giulio, Paola, Fumagalli, Roberto, Labarta, Violeta, Latini, Roberto, Gattinoni, Luciano, Malacrida, Roberto, Mascheroni, Daniele, Pelosi, Paolo, Pesenti, Antonio, Taccone, Paolo and Tognoni, Gianni. 2001. Effect of Prone Positioning on the Survival of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure. The New England Journal of Medicine. 345: (8)568-573.